What happened last week with the Fed speakers?
Powell blessed multiple 50bp hikes, while Bullard is even thinking of 75bps hike
Opinions expressed are solely my own and do not express the views or opinions of my employer.
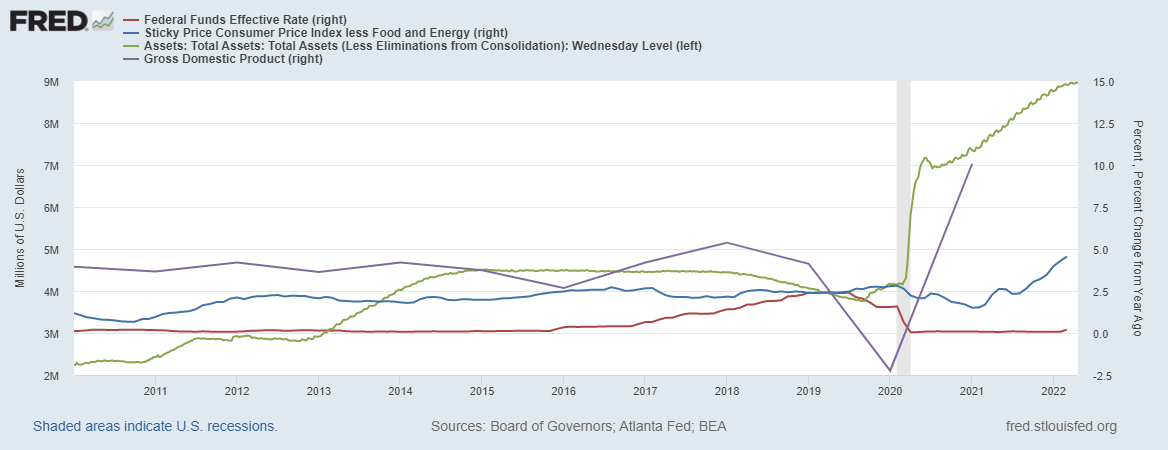
Fed Chairman Jerome Powell, along with a couple of other Fed officials are prepared to shift monetary tightening into a higher gear. What does that mean? it means that the Fed will increase the Fed Fund Rates to “neutral,” or probably a bit more. At a neutral rate, the economy should be stable ie the economy will not be boosted nor its growth will be restricted. Most Fed officials assume the rate to be close to 2.5%, but no one knows where this neutral rate should be. The Fed also plans to solidify its plan to shrink its $9 trillion Balance Sheet, which should tighten the Financial conditions along with the rate hikes.
Ok, so how many rate hikes does the market expect? 10 hikes of 25bps by December 2022, and the expectation is that we will be close to 3.4% from the current rate of 0.25% by December 2023 as per Eurodollar Futures market.
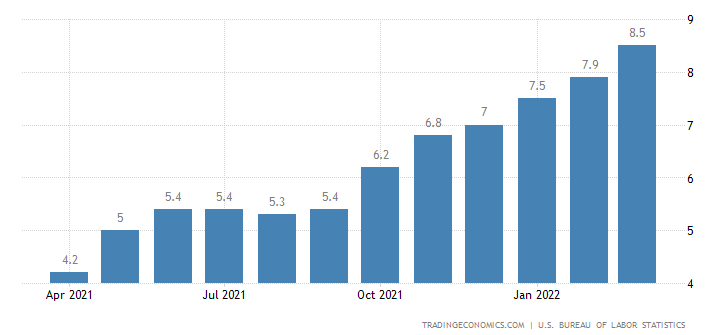
Is that enough to bring inflation down from the whopping 8.5%? Only time will tell, as monetary policies take time to impact the real economy. Further, China’s COVID lockdowns and the war in Ukraine have made things a bit worse, as we were expecting to see some relief from higher prices by now, but here we are…
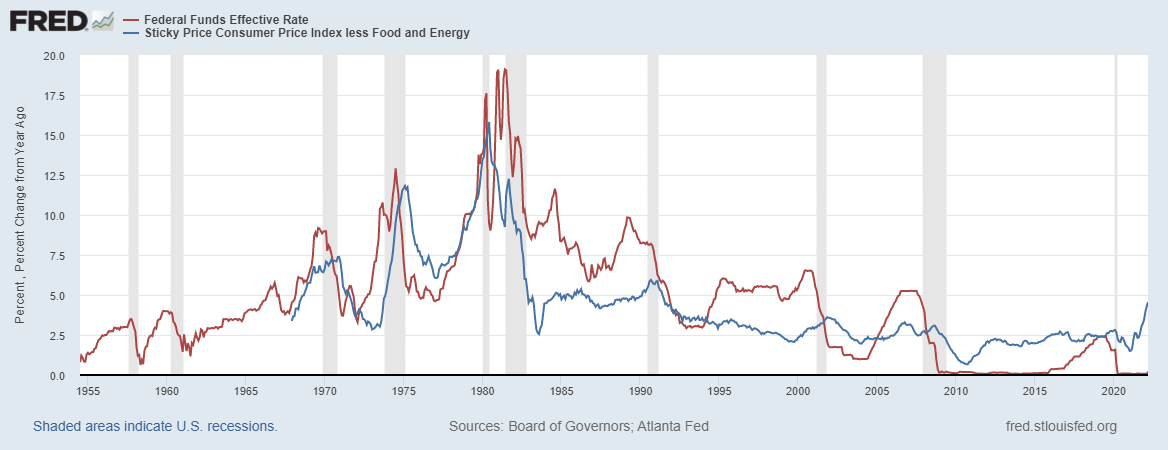
And if the inflation doesn’t come down as expected, what will the Fed do? They will continue to use their “tools,” specifically interest rate hikes, and liquidate the massive Balance Sheet. We don’t have a recent experience of the Fed tightening the monetary policy to control the run-off inflation, but during Paul Volcker’s era, we did raise the Fed Funds Rate close to 19%
Ok. What can go wrong? ‘Policy error’ is the lingo used by most market participants. It is when the Fed overtightens, which leads to a slower growth phase and perhaps a recession. For context, the last time the FOMC raised interest rates and executed their plan to reduce Balance sheet holdings (BS runoff), they ended up over-tightening ie growth slowed and inflation declined. They ended up reversing course and eased the financial conditions by cutting rates and shoring up the Balance Sheet.
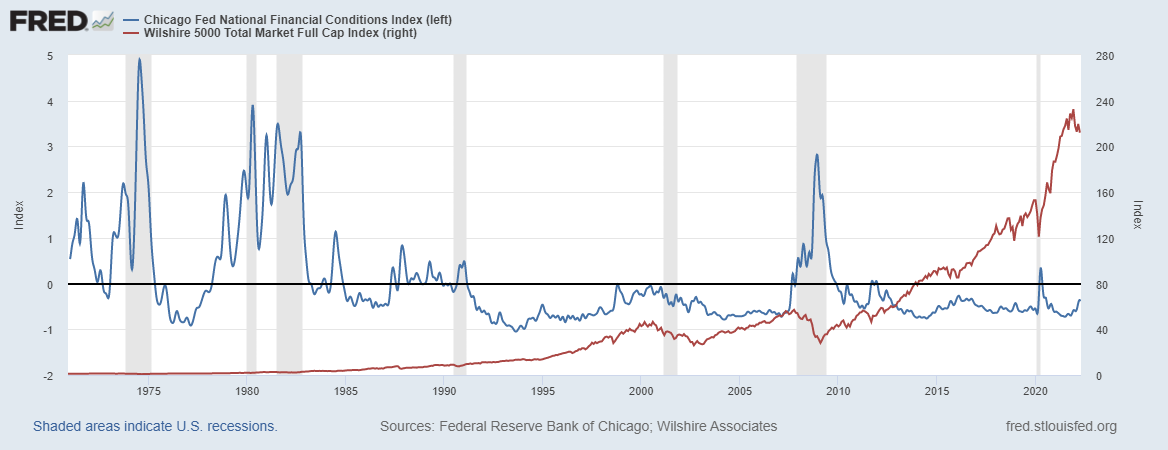
How does the Fed know that its policy is having the desired effects on the economy? They monitor the financial conditions index, such as the Chicago Fed's National Financial Conditions Index (NFCI) which provides a comprehensive weekly update on U.S. financial conditions in money markets, debt and equity markets, and the traditional and "shadow" banking systems. Positive values of the NFCI indicate financial conditions that are tighter than average, while negative values indicate financial conditions that are looser than average.
Bottom line: Fed is clearly worried about inflation, and will take steps to regain its credibility after getting the ‘transitory’ narrative wrong. Meanwhile, Russia/Ukraine war is now expected to be more of a prolonged conflict, which implies that commodity prices are expected to remain elevated for some time.